看AlphaZero的时候看到这个mcts,因为需要用他来产生棋局进行训练。比较神奇,就小小探究一下。这边做一个五子棋mcts AI。
mcts按我目前的理解也就是在目前的情况下(根节点),随机产生下一步的节点,之后进行随机模拟至产生一个结果,把结果反馈于当前节点与之前的节点,这样模拟n次以后,得到根节点的下一步的各个节点的A/B,A为结果获胜的次数,B为访问次数。 用公式计算就可以得到各个节点的收益,得到收益最大的节点并进行选中。盗图如下,不过图中有多层节点,需计算也就更大。
用公式计算就可以得到各个节点的收益,得到收益最大的节点并进行选中。盗图如下,不过图中有多层节点,需计算也就更大。

直接上代码
from math import *
import random
#python3
#如果要改写其他游戏,主要编写下面这个class就可以
class Chess:
#初始化游戏状态
def __init__(self,cl):
self.cl=cl
self.all_n=cl*cl
self.playerJustMoved = 2
self.place=[0]*self.all_n
#复制游戏状态作为子节点
def Clone(self):
st = Chess(self.cl)
st.playerJustMoved = self.playerJustMoved
st.place=self.place[:]
return st
#进行游戏的下一步
def DoMove(self,state):
self.playerJustMoved = 3 - self.playerJustMoved
self.place[state]=self.playerJustMoved
#获取游戏可移动状态
def GetMoves(self):
""" Get all possible moves from this state.
"""
return [i for i in range(self.all_n) if self.place[i] == 0]
#检查是否游戏结束
def checkout(self):
for i in range(self.all_n):
if self.place[i]!=0 and self.check(i):
return True
return False
#检查五子棋
def check(self,z):
y=int(z/self.cl)
x=z-y*self.cl
mid=self.place[x+y*self.cl]
if (x<2 and y<2) or (x<2 and y>self.cl-3) or (x>self.cl-3 and y>self.cl-3) or (x>self.cl-3 and y<2):
return False
elif x<2 or x>self.cl-3:
if mid==self.place[x+(y-1)*self.cl] and mid==self.place[x+(y-2)*self.cl] and mid==self.place[x+(y+1)*self.cl] and mid==self.place[x+(y+2)*self.cl]:
return True
elif y<2 or y>self.cl-3:
if mid==self.place[x-1+y*self.cl] and mid==self.place[x-2+y*self.cl] and mid==self.place[x+1+y*self.cl] and mid==self.place[x+2+y*self.cl]:
return True
else:
if mid==self.place[x+(y-1)*self.cl] and mid==self.place[x+(y-2)*self.cl] and mid==self.place[x+(y+1)*self.cl] and mid==self.place[x+(y+2)*self.cl]:
return True
if mid==self.place[x-1+y*self.cl] and mid==self.place[x-2+y*self.cl] and mid==self.place[x+1+y*self.cl] and mid==self.place[x+2+y*self.cl]:
return True
if mid==self.place[x-1+(y-1)*self.cl] and mid==self.place[x-2+(y-2)*self.cl] and mid==self.place[x+1+(y+1)*self.cl] and mid==self.place[x+2+(y+2)*self.cl]:
return True
if mid==self.place[x-1+(y+1)*self.cl] and mid==self.place[x-2+(y+2)*self.cl] and mid==self.place[x+1+(y-1)*self.cl] and mid==self.place[x+2+(y-2)*self.cl]:
return True
#得到游戏结果,这边主要得到模拟结果用作反馈
def GetResult(self, playerjm):
""" Get the game result from the viewpoint of playerjm.
"""
for i in range(self.all_n):
if self.place[i]!=0 and self.check(i):
if self.place[i] == playerjm:
return 1.0
else:
return 0.0
if self.GetMoves() == []:
return 0.5 # draw
assert False
#mcts算法节点部分
class Node:
""" A node in the game tree. Note wins is always from the viewpoint of playerJustMoved.
Crashes if state not specified.
"""
def __init__(self, move = None, parent = None, state = None):
self.move = move # the move that got us to this node - "None" for the root node
self.parentNode = parent # "None" for the root node
self.childNodes = []
self.wins = 0
self.visits = 0
self.untriedMoves = state.GetMoves() # future child nodes
self.playerJustMoved = state.playerJustMoved # the only part of the state that the Node needs later
def UCTSelectChild(self):
""" Use the UCB1 formula to select a child node. Often a constant UCTK is applied so we have
lambda c: c.wins/c.visits + UCTK * sqrt(2*log(self.visits)/c.visits to vary the amount of
exploration versus exploitation.
"""
s = sorted(self.childNodes, key = lambda c: c.wins/c.visits + sqrt(2*log(self.visits)/c.visits))[-1]
return s
def AddChild(self, m, s):
""" Remove m from untriedMoves and add a new child node for this move.
Return the added child node
"""
n = Node(move = m, parent = self, state = s)
self.untriedMoves.remove(m)
self.childNodes.append(n)
return n
def Update(self, result):
""" Update this node - one additional visit and result additional wins. result must be from the viewpoint of playerJustmoved.
"""
self.visits += 1
self.wins += result
def __repr__(self):
return "[M:" + str(self.move) + " W/V:" + str(self.wins) + "/" + str(self.visits) + " U:" + str(self.untriedMoves) + "]"
def TreeToString(self, indent):
s = self.IndentString(indent) + str(self)
for c in self.childNodes:
s += c.TreeToString(indent+1)
return s
def IndentString(self,indent):
s = "\n"
for i in range (1,indent+1):
s += "| "
return s
def ChildrenToString(self):
s = ""
for c in self.childNodes:
s += str(c) + "\n"
return s
#mcts算法模拟部分
def UCT(rootstate, itermax, verbose = False):
""" Conduct a UCT search for itermax iterations starting from rootstate.
Return the best move from the rootstate.
Assumes 2 alternating players (player 1 starts), with game results in the range [0.0, 1.0]."""
rootnode = Node(state = rootstate)
for i in range(itermax):
node = rootnode
state = rootstate.Clone()
# Select
while node.untriedMoves == [] and node.childNodes != []: # node is fully expanded and non-terminal
node = node.UCTSelectChild()
state.DoMove(node.move)
# Expand
if node.untriedMoves != []: # if we can expand (i.e. state/node is non-terminal)
m = random.choice(node.untriedMoves)
state.DoMove(m)
node = node.AddChild(m,state) # add child and descend tree
# Rollout - this can often be made orders of magnitude quicker using a state.GetRandomMove() function
while state.GetMoves() != []: # while state is non-terminal
state.DoMove(random.choice(state.GetMoves()))
# Backpropagate
while node != None: # backpropagate from the expanded node and work back to the root node
node.Update(state.GetResult(node.playerJustMoved)) # state is terminal. Update node with result from POV of node.playerJustMoved
node = node.parentNode
# Output some information about the tree - can be omitted
#if (verbose): print rootnode.TreeToString(0)
#else: print rootnode.ChildrenToString()
#print(rootnode.childNodes)
return sorted(rootnode.childNodes, key = lambda c: c.visits)[-1].move # return the move that was most visited
#主函数
def UCTPlayGame():
itermax=5000#每一步迭代的次数,越多越准确,但这边只有单分支,应该会有一个上限
length=8#棋盘长宽
res=["_"]*length*length
state = Chess(length)
save_state=""
while (not state.checkout() and state.GetMoves()!=[]):
if state.playerJustMoved == 1:
m = UCT(rootstate = state, itermax = itermax, verbose = False) #2
print("电脑2下子("+str(m-int(m/length)*length)+" "+str(int(m/length))+")")
res[m]="X"
else:
m = UCT(rootstate = state, itermax = itermax, verbose = False) #1
print("电脑1下子("+str(m-int(m/length)*length)+" "+str(int(m/length))+")")
#如果想自己和电脑下就注释掉上面两行,再去掉下面两个注释。
#my=input("您下子(格式如:3 4)\n").split(" ")
#m=int(my[0])+int(my[1])*length
res[m]="O"
print("Best Move: " + str(m) + "\n")
for i in range(length):
print(" ".join(res[length*i:length*(i+1)]))
state.DoMove(m)
if state.GetResult(state.playerJustMoved) == 1.0:
print("Player " + str(state.playerJustMoved) + " wins!")
elif state.GetResult(state.playerJustMoved) == 0.0:
print("Player " + str(3 - state.playerJustMoved) + " wins!")
else: print("Nobody wins!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
""" Play a single game to the end using UCT for both players.
"""
UCTPlayGame()
实验结果:
以8*8棋盘为例,在每步迭代几千次之后,电脑就基本可以学会档这个技能,但电脑要赢这边还是有点困难,没有多步的规划。
有时候也会莫名下到棋盘边上的点,想想棋盘边上的点赢的概率应该低吧。这个可能步数不够或者模拟有问题。实验如下图:
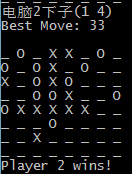
灵感来源:知乎某讲篇AlphaZero的文章
算法代码借鉴:mcts.ai
版权声明:本文为原创文章,转载请注明出处和作者,不得用于商业用途,请遵守
CC BY-NC-SA 4.0协议。
赞赏一下
 支付宝打赏
支付宝打赏 微信打赏
微信打赏